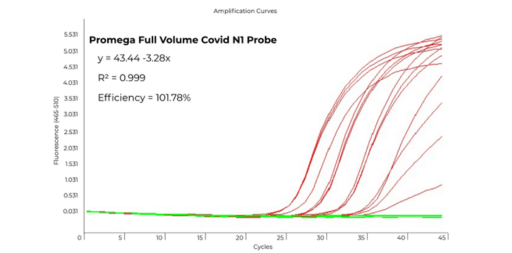
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) has revolutionized biological research, particularly in genetic engineering and diagnostics. Owing to its adaptability, PCR can be tailored to suit a wide array of applications, the most remarkable being quantification of nucleic acid sequences - both relative (quantitative PCR or qPCR) and absolute (digital PCR or dPCR).
The core process of PCR is divided into two essential steps: liquid handling and thermal cycling. The liquid handling step involves transferring samples and precisely dispensing key reaction components, including buffers, enzymes, primers, probes, and dNTPs into individual wells of the PCR plate. This initial step sets the foundation for the subsequent thermal cycling process, where temperature variations enable amplification.
Liquid handling steps in PCR workflows
Manually pipetting low-volume ingredients can introduce inconsistencies due to user variability, especially with the high precision required for PCR protocol setups. Moreover, high throughput experiments demand miniaturized reactions, and the imprecision of manual pipettes is more pronounced at sub-microliter volumes. Also, processing large sample batches manually is time-consuming, reduces workflow efficiency, and raises the risk of cross-contamination. Although manual pipetting seems cost-effective, time inefficiency, the potential for errors, low volume limitations, and associated reagent wastage add to unwanted expenditure. To overcome these challenges, automated liquid handling (ALH) offers a more reliable approach for reproducible results.
Formulatrix ALH for PCR Protocol Setup
Formulatrix's ALH systems redefine PCR protocol setup by combining precision, reaction miniaturization, and high throughput.
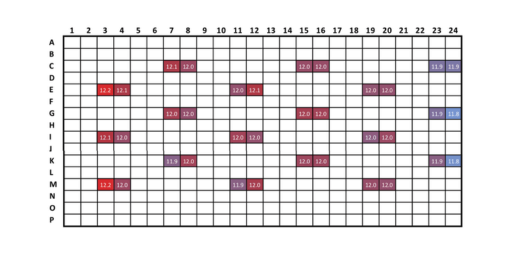
- Precision: Precise volume transfers as low as 100 nL with a CV of <2%, ensuring consistent and reliable results
- Reaction miniaturization: Minimize waste with dead volumes as low as 6 µL, perfect for miniaturized PCR reactions and conserving valuable samples
- High Throughput: Compatible with standard and custom plate formats, including 384- and 1536-well plates, to meet diverse application needs
- Streamlined Integration: Features like CSV file compatibility and API integration simplify workflows and enable seamless high throughput processing
| PCR Workflow Liquid Handling Features |
Formulatrix ALH Mantis Tempest F.A.S.T. FLO i8 PD |
|---|---|
| PCR Components Transfer | ✔ ✔ ✔ ✔ |
| Sample Transfer | ✔ ✔ ✔ ✔ |
| Buffer Transfer | ✔ ✔ ✔ ✔ |
| Concentration Normalization | ✔ ✔ ✔ ✔ |
| Serial Dilution | ✔ ✔ |
| Sample Pooling | ✔ ✔ |
| Plate Stamping | ✔ ✔ |
| Plate Reformatting | ✔ ✔ |
| Beads Transfer | ✔ ✔ ✔ ✔ |
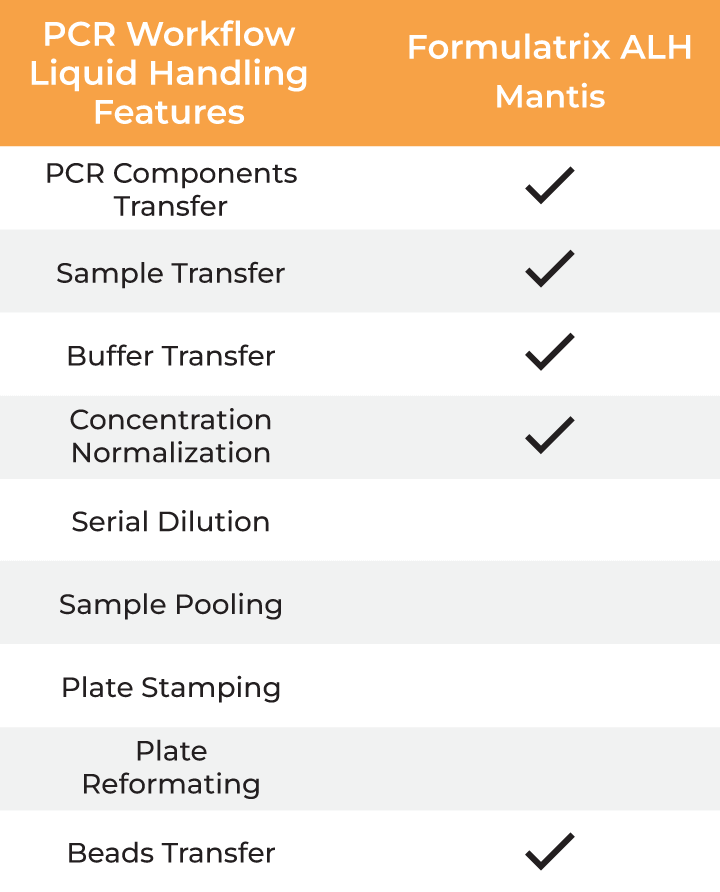
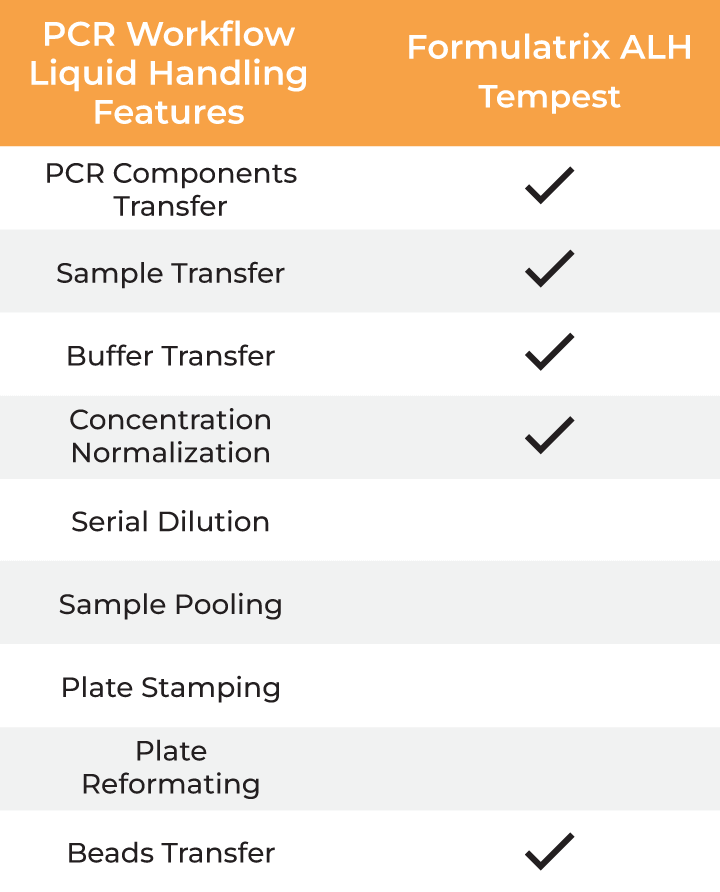
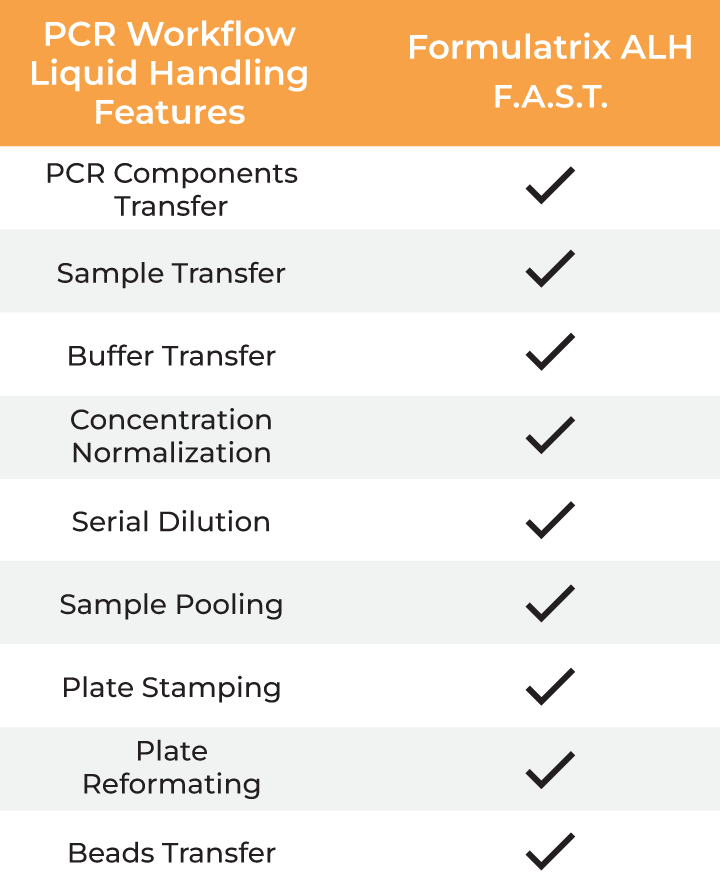
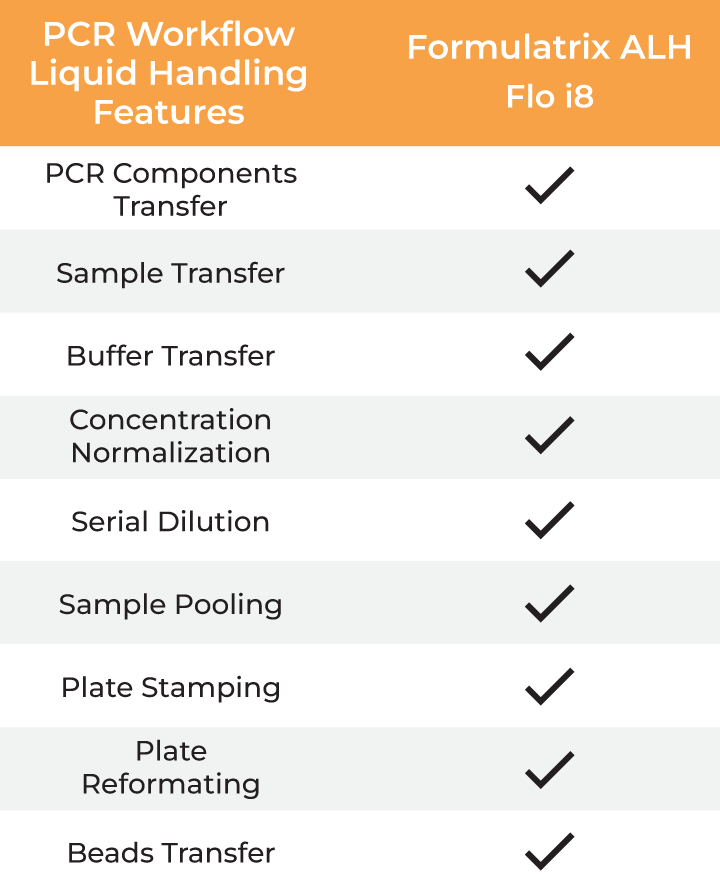
Formulatrix ALH features for PCR workflows
Webinars
Learn how the Mantis reduces consumable tip usage for diagnostics, and reliably miniaturizes qPCR assays to reduce reagents consumption.
Application Notes
Explore how the Mantis reduces pipette tip usage and enables precise low-volume dispensing for effective assay miniaturization.
Discover precise, accurate, and contamination-free dispensing for qPCR and NGS workflows, including sample normalization for consistent results.